
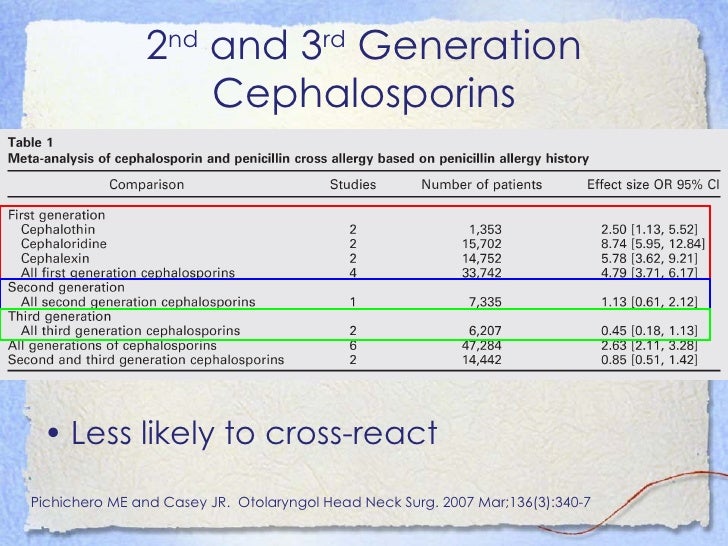
(D) Summary Statement 95: Patients with a history of an immediate-type reaction to 1 cephalosporin should avoid cephalosporins with similar R-group side chains.
Penicillin cephalosporin cross reactivity skin#
(D) A negative skin test result does not rule out an allergy because the negative predictive value is unknown. (D) Summary Statement 94: Skin testing with native cephalosporins is not standardized, but a positive skin test result using a nonirritating concentration suggests the presence of drug specific IgE antibodies. (C) Summary Statement 93: Most hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins are probably directed at the R-group side chains rather than the core beta-lactam portion of the molecule. Summary Statement 92: The overall reaction rate to cephalosporins is approximately 10-fold lower than it is for penicillin. Summary Statement 71: Approximately 10% of patients report a history of penicillin allergy, but after complete evaluation, up to 90% of these individuals are able to tolerate penicillins. Some quotes from the 2010 Practice Parameter for Drug Allergy with evidence basis provided in parenthesis are: (Annè, Macy) Finally there is evidence of increased risk for any medication, irrespective of structure similarities or cross-reactivity, if there is history of prior drug reaction (Strom). (Romano Kelkar Mirakian) However, other analyses minimize risk. The medical literature suggests there is greater risk in giving cephalosporin, particularly first generation cephalosporin, to a patient with a history of penicillin allergy than to a patient without penicillin allergy (2-4 fold increased risk). The difficulty in answering your question is the meaning of “safe” and the meaning of “penicillin allergic patient”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
